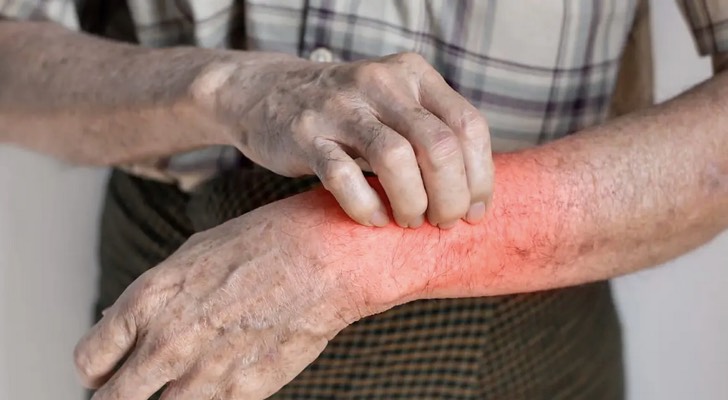
Atopic dermatitis (AD), commonly known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects people of all ages, including seniors. While often associated with children, AD can persist into adulthood or even develop later in life. For older adults, the condition can present unique challenges, impacting both physical and emotional well-being. Understanding these effects can help seniors and their caregivers manage the condition effectively.
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis in Seniors
Atopic dermatitis is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. Seniors may experience more severe symptoms due to age-related changes in skin structure and function. As the skin becomes thinner and loses moisture with age, it becomes more prone to irritation, infections, and delayed healing. Additionally, weakened immune responses in older adults can exacerbate symptoms, making flare-ups more frequent and harder to control.
Physical Health Impacts
Seniors with AD often struggle with intense itching, which can lead to excessive scratching, causing skin damage, infections, and discomfort. In severe cases, chronic inflammation can result in thickened, scaly skin or painful cracks that increase the risk of bacterial infections. Sleep disturbances are also common due to persistent itchiness, leading to fatigue and reduced overall quality of life.
Another concern is the potential impact on pre-existing conditions. Seniors with diabetes or cardiovascular diseases may experience worsened symptoms when dealing with chronic skin inflammation. Moreover, certain medications commonly used by older adults may trigger or aggravate AD symptoms, making proper medical guidance crucial.
Emotional and Mental Well-Being
Beyond physical discomfort, AD can also take a toll on a senior’s mental health. The persistent itch and visible skin changes may lead to embarrassment, social withdrawal, anxiety, or depression. Many seniors with AD report feelings of frustration due to the chronic nature of the condition and the challenges of managing symptoms effectively.
Managing Atopic Dermatitis in Seniors
Effective management of AD in older adults requires a combination of skincare, lifestyle adjustments, and medical treatments. Here are some key approaches:
- Gentle Skincare Routine: Using mild, fragrance-free moisturizers and cleansers helps maintain skin hydration and reduce irritation.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and eliminating common irritants such as harsh soaps, allergens, and extreme temperatures can help prevent flare-ups.
- Medications & Treatments: Prescription creams, antihistamines, or newer biologic treatments may be necessary for severe cases. Consulting a dermatologist is essential for personalized treatment plans.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, proper hydration, and stress management techniques can contribute to better skin health.
Final Thoughts
Atopic dermatitis in seniors is more than just a skin condition—it can significantly impact overall health and well-being. By understanding its effects and taking proactive steps for management, seniors can maintain a better quality of life despite the challenges of AD. Whether through skincare, medical treatment, or lifestyle changes, proper care and support are key to minimizing its impact.
 © Copyright 2025 Shirabe-ru | Terms | Privacy Policy | Contact Us
© Copyright 2025 Shirabe-ru | Terms | Privacy Policy | Contact Us